Search
An interventional birth cohort researching ways to optimise health and identify conditions that enable every child to flourish from an early age.
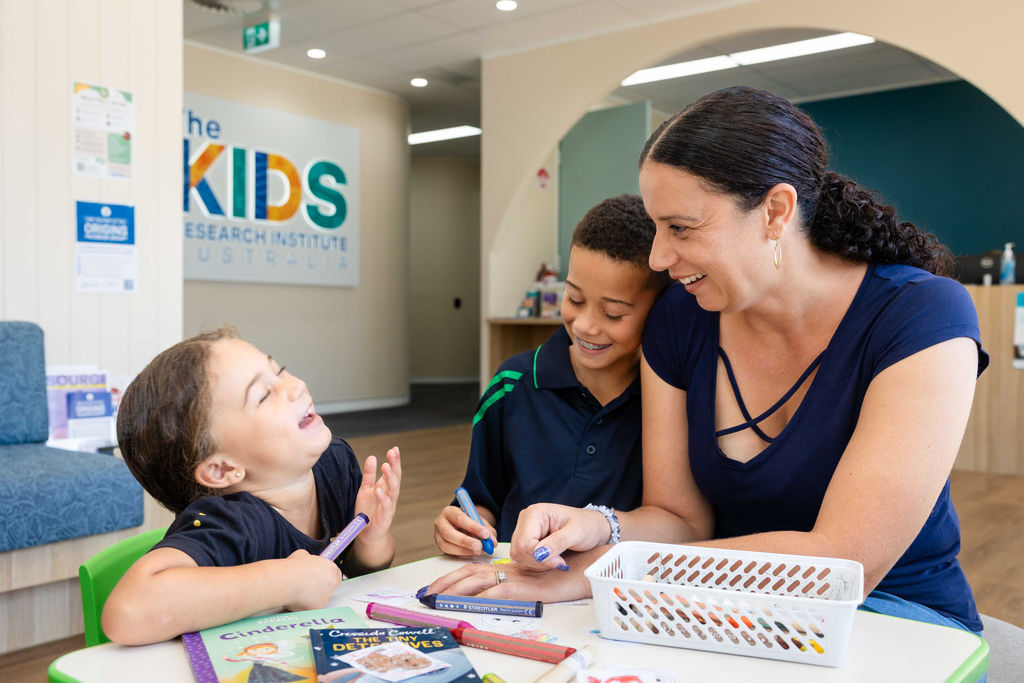

A unique national platform delivering faster research at scale to improve the health, wellbeing and equity of children and their parents across Australia

News & Events
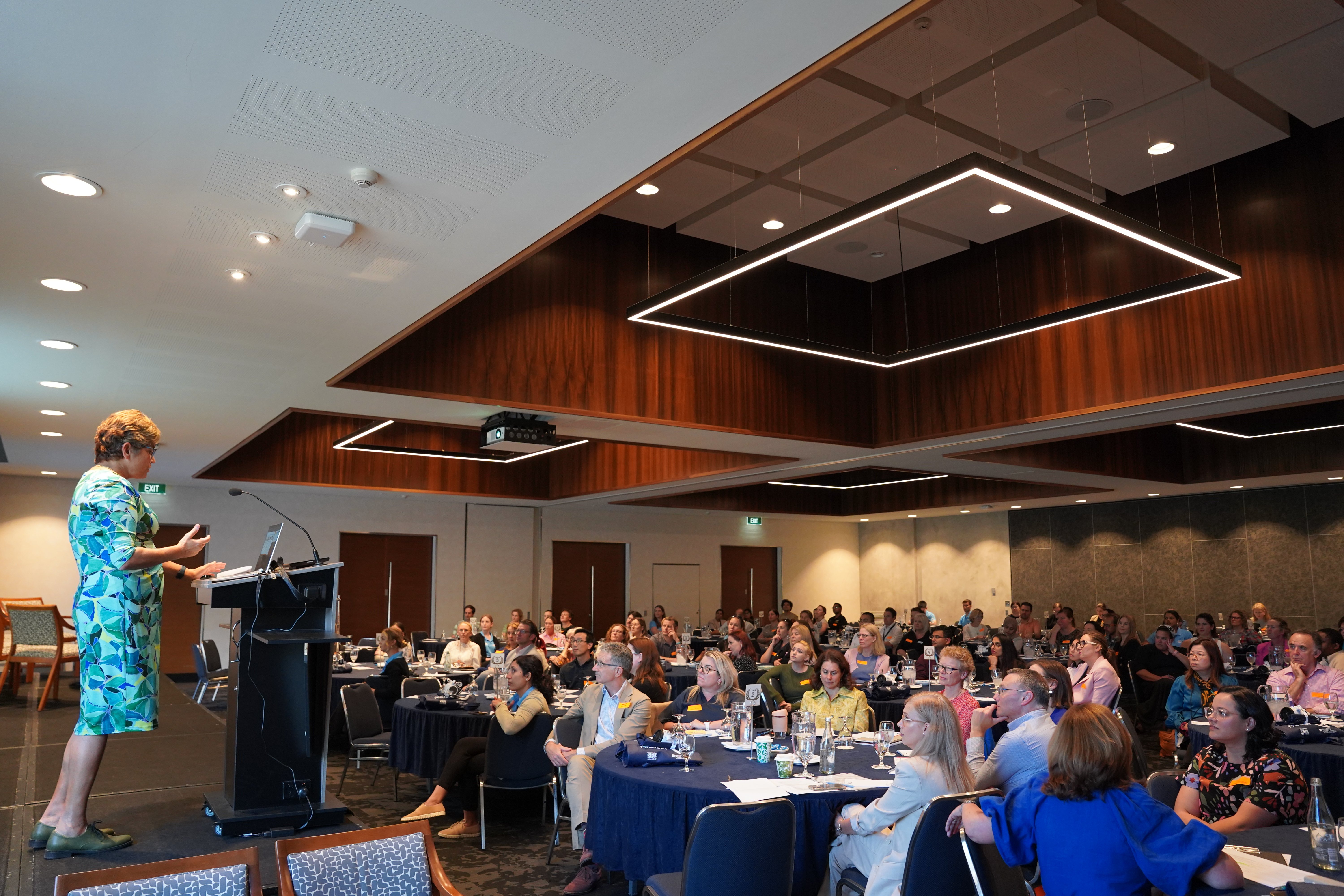
The Power of Longitudinal Cohorts – The 2024 ORIGINS ShowcaseYesterday, we were delighted to host close to 200 people at The ORIGINS 2024 Showcase, which explored the power of longitudinal cohorts, now and in

News & Events
Better Your BioMood: First Findings Published in Origins SubprojectFirst Findings Published in Origins Sub-Project

News & Events
Child has COVID? A reminder to think ORIGINS!ORIGINS is on the lookout for our Long COVID Study. As we enter a new wave of COVID in the community, we would like to remind participants to 'think

News & Events
ORIGINS named in multi-million dollar investment towards child healthORIGINS named in multi-million investment towards child health

News & Events
ORIGINS Family Fun Day 2023Families gathered in the autumn sunshine to celebrate ORIGINS
News & Events
Changing advice for parents on food allergiesDr Debbie Palmer spoke to Ch7 Sunrise about the changing advice for parents about the development of food allergies in kids.

News & Events
Nature Play & Grow - based on science but promoting playA pilot program, teaching families how to 'play' in nature, has been shown to be effective in helping families unlock the mental and physical health benefits of connecting with nature and community through outdoor play, easily, and locally.

News & Events
HBF and ORIGINS Helping Fathers to FlourishA new partnership with HBF will help fathers in their transition to parenthood
