Search
Showing results for "aboriginal respiratory"
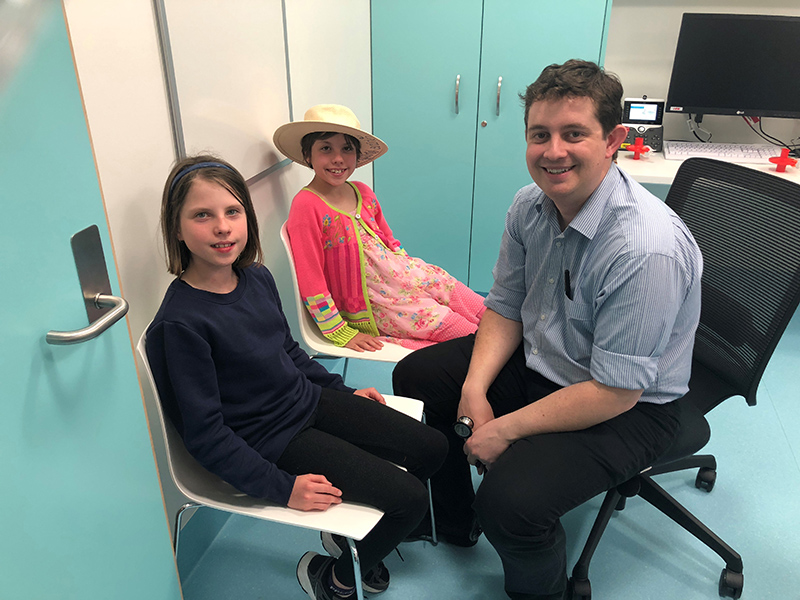

The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers are investigating whether a simple urine test could predict whether young children with wheezing symptoms will go on to develop asthma.
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the small and large conducting airway mucosa characterised by Th2 cell immunity.
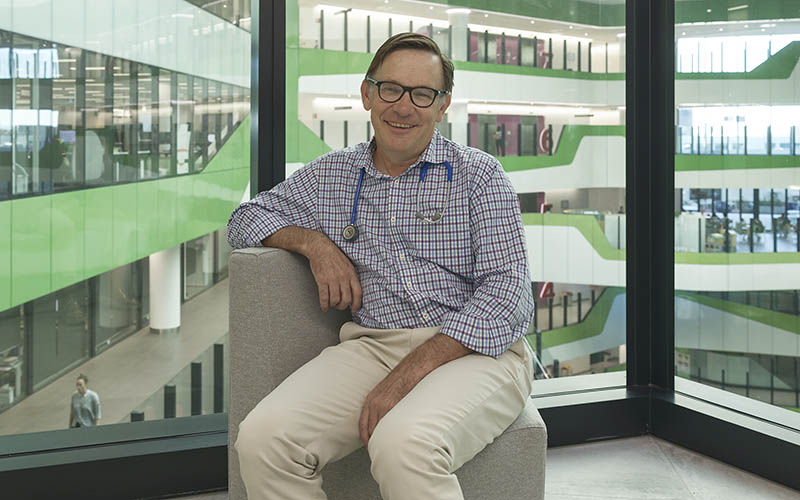

Global circulation of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is shaped by human air travel with travellers hosting new strains fuelling transmission across borders, an international The Kids Research Institute Australia study found.
A The Kids Research Institute Australia study has suggested the seasonal flu vaccine for children could also protect them from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), with the dual benefit easing pressure on hospitals.

The Kids Research Institute Australia strongly supports the Federal Government’s announcement today to introduce a suite of reforms aimed at banning non-prescription vaping products in Australia.
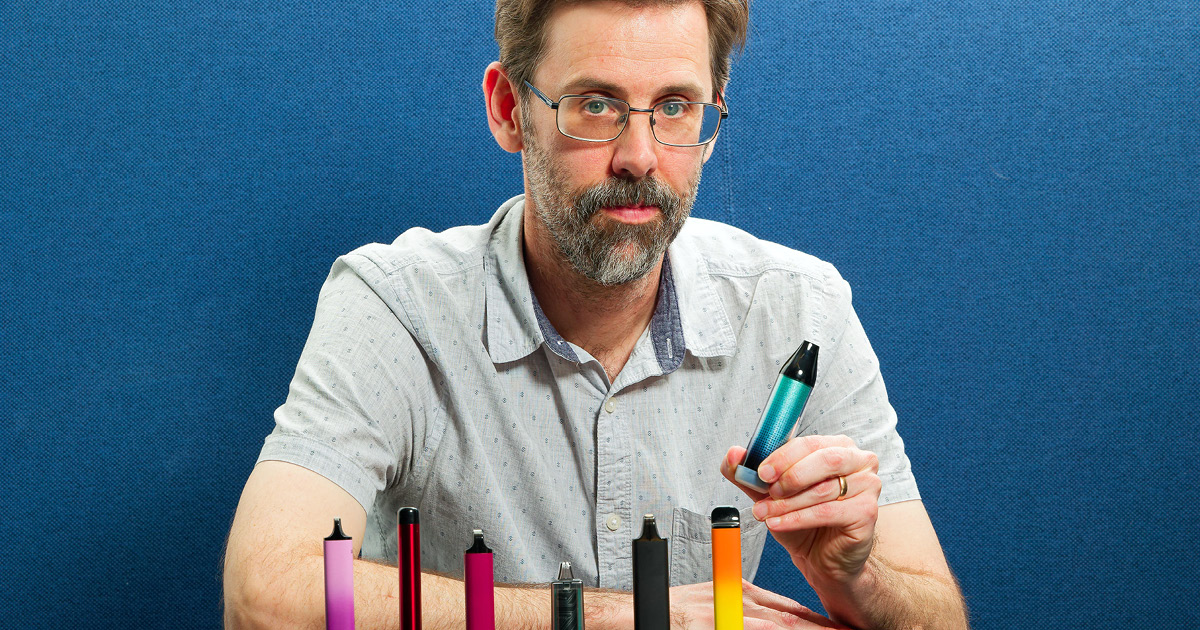

Formative research undertaken by The Kids Research Institute Australia has helped inform tough new laws introduced by the Federal Government to reduce the harm caused by vapes.
Active nasal surveillance culture (ANSC) is recognized to enable rapid detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the intensive care unit (ICU), which can contribute to the prevention of Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). This study aims to evaluate the usefulness of ANSC in assessing the development of VAP in ICU patients.
Estimate the global prevalence of neurodevelopmental impairment in children with Robin sequence (RS) at one year or more of age.
Ensitrelvir, a 3C-like protease inhibitor, received emergency approval in Japan in November 2022 for treating non-hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. However, confirmation of its real-world clinical effectiveness is limited.
We present lung virome data recovered through shotgun metagenomics in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from an infant with cystic fibrosis, who tested positive for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infection. Using a bioinformatic pipeline for virus characterization in shotgun metagenomic data, we identified five viral contigs representing Pseudomonas phages classified as Caudoviricetes.
