Search

News & Events
Thinking of The Kids is central to child health research institute rebrandWestern Australia’s biggest and only medical research institute dedicated to improving kids’ health and wellbeing has rebranded to The Kids Research Institute Australia.

News & Events
2024 Run for a Reason – Team The KidsThe HBF Run for a Reason is back and if you’re looking for a reason to take part in this year’s event, let it be child health research.

News & Events
New national trial leverages childcare to boost physical activity in young Aussie kidsMore than 80,000 Australian children are expected to benefit as 700 childcare centres across the country trial a new program aimed at boosting declining physical activity levels.

News & Events
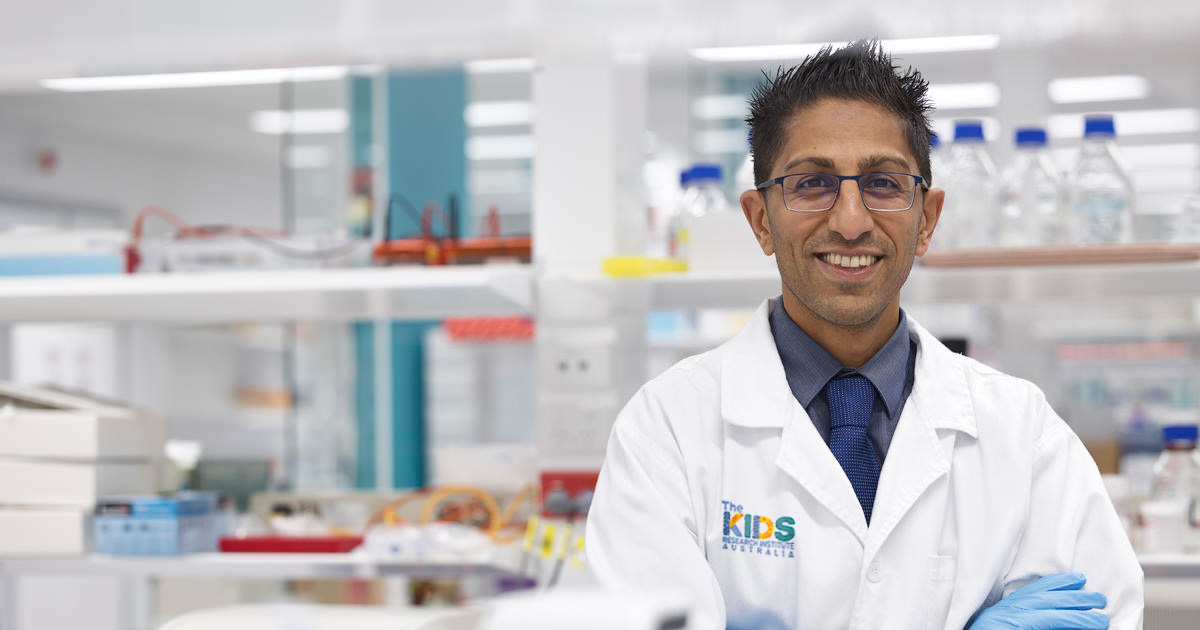
Pioneering paediatric oncologist receives top cancer research awardAssociate Professor Rishi Kotecha, Co-Head of Leukaemia Translational Research at The Kids Research Institute Australia Cancer Centre and Consultant Paediatric Oncologist at Perth Children's Hospital, has been named Cancer Council WA’s 2024 Cancer Researcher of the Year.
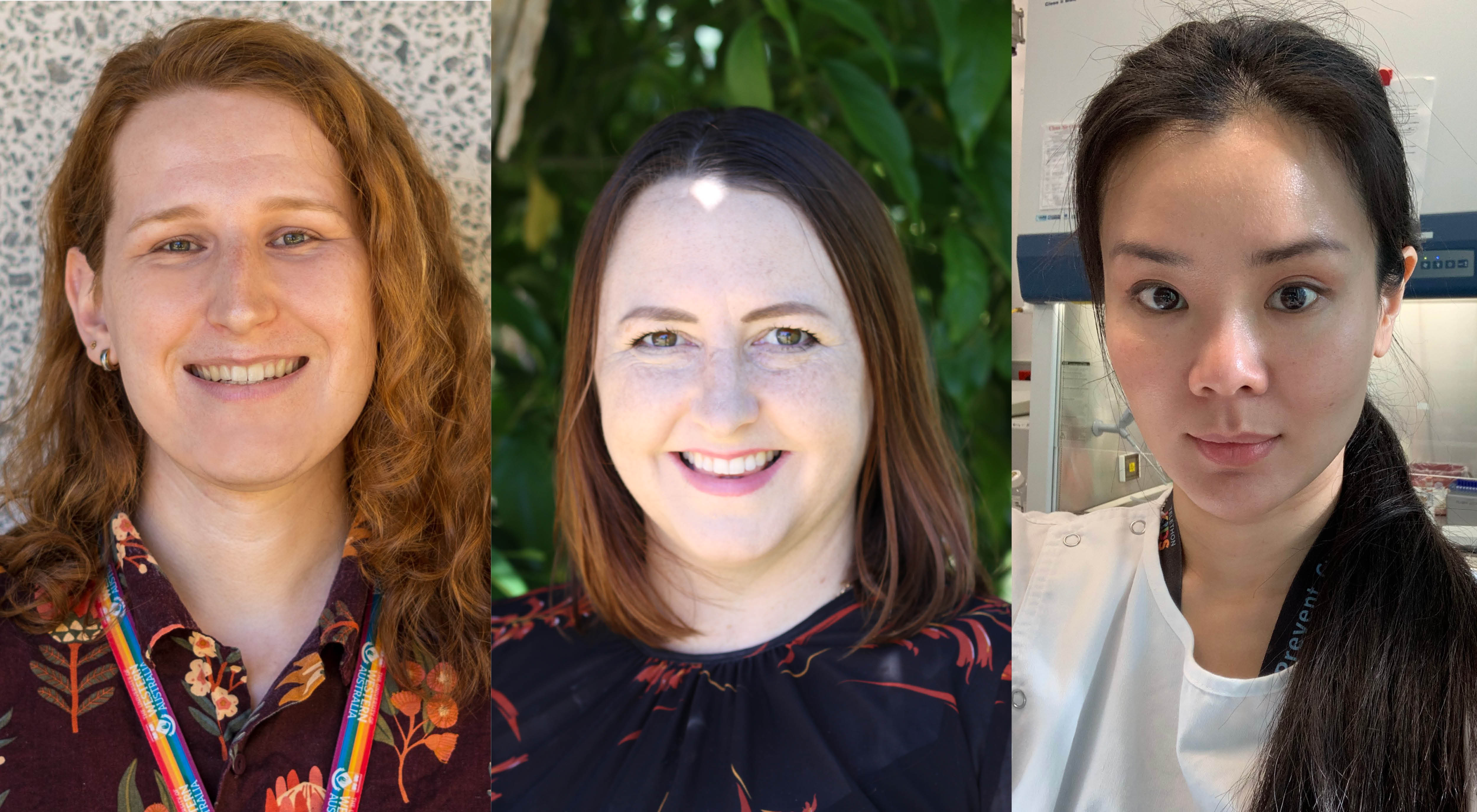

News & Events
Major funding announced to kickstart key WCVID projectsThe Wesfarmers Centre of Vaccines and Infectious Diseases (WCVID) awarded three successful recipients with Catalyst research grants, with each researcher receiving $80,000 towards their chosen project.
News & Events
Prestigious honour for Indigenous Genomics leaderTrailblazing Aboriginal doctor and health researcher Professor Alex Brown has been made a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Engineering (ATSE) in recognition of his leadership in ensuring Indigenous peoples are at the forefront of genomics efforts nationally and internationally.

News & Events
Beyond the horizon: improving cancer outcomes for Indigenous childrenDr Jessica Buck, a researcher at The Kids Research Institute Australia Cancer Centre and a Kamilaroi woman, is on a mission to address the unique challenges faced by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children with cancer.

News & Events
Researchers share in almost $3 million for groundbreaking child health researchFive researchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia will share in almost $3 million in grants to continue groundbreaking research to tackle childhood cancer, asthma prevention, lung disease and chronic ear infections.

News & Events
Research breakthrough gives hope to children with rare and undiagnosed diseasesA complex five-year experiment which cracked the code of a genetic mystery has paved the way for faster and more accurate diagnoses of the most rare and unknown diseases affecting children.
News & Events
Prestigious invite for WA infectious disease expertsTwo Perth clinician-scientists have been recognised as national leaders in infectious disease research after being elected as Fellows of the esteemed Australian Academy of Health and Medical Sciences.
