Search

Western Australia’s sudden hard lockdown came without warning and unlike when COVID-19 first kept us at home last year, there are now rules on how long we can spend exercising outside.
Plenty of parents will tell you the daily lunchbox dilemma is one thing they did not miss during the summer holidays.
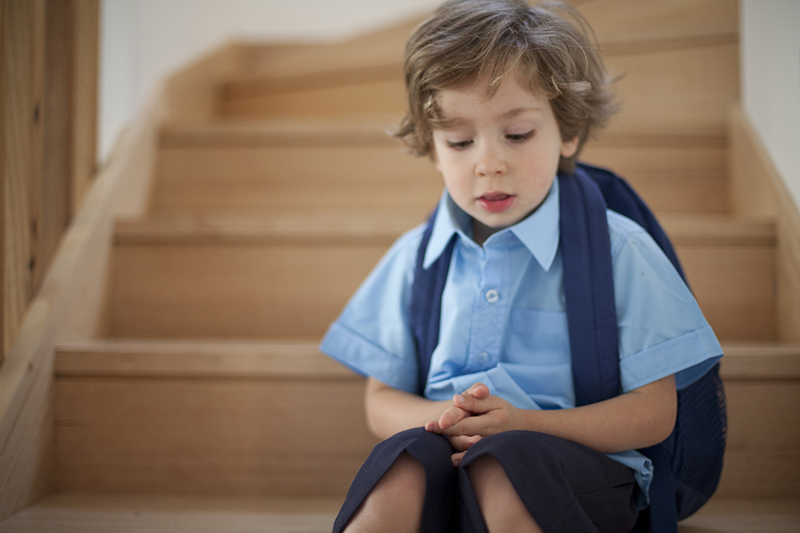

It is natural for children to feel anxious about what a new school year will bring. Here's how to help make the first days and weeks easier on your child and the whole family.

Year 7 is a time of big change and challenges - and it's also the best time to start talking about alcohol.
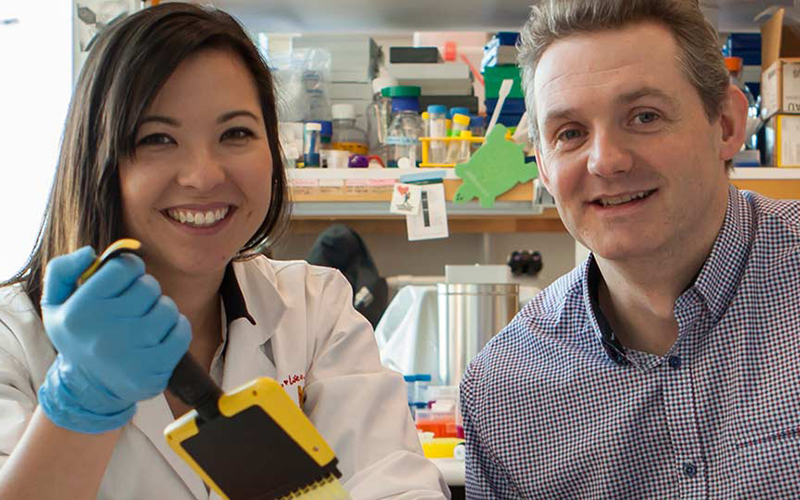

A new combination of drugs could help to increase survival rates with fewer side effects for some children with one of the most aggressive forms of childhood brain cancer.

The Kids Research Institute Australia has welcomed the announcement of a new National Agreement on Closing the Gap.
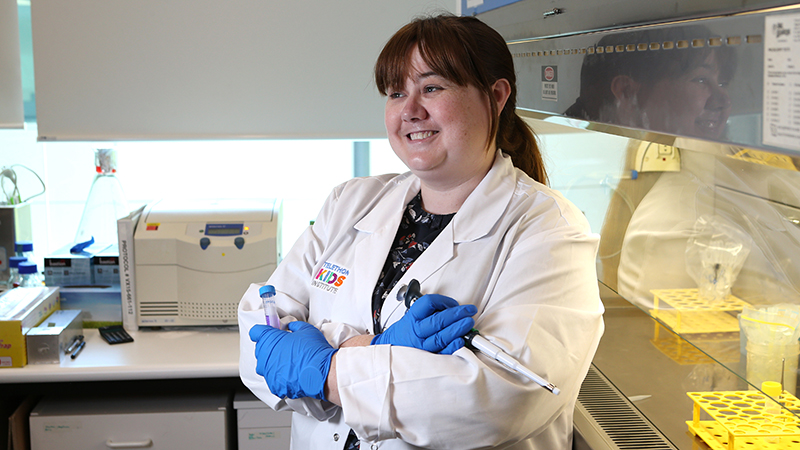

New research by The Kids shows donor immune cells are highly effective at boosting the body’s response against leukaemia.
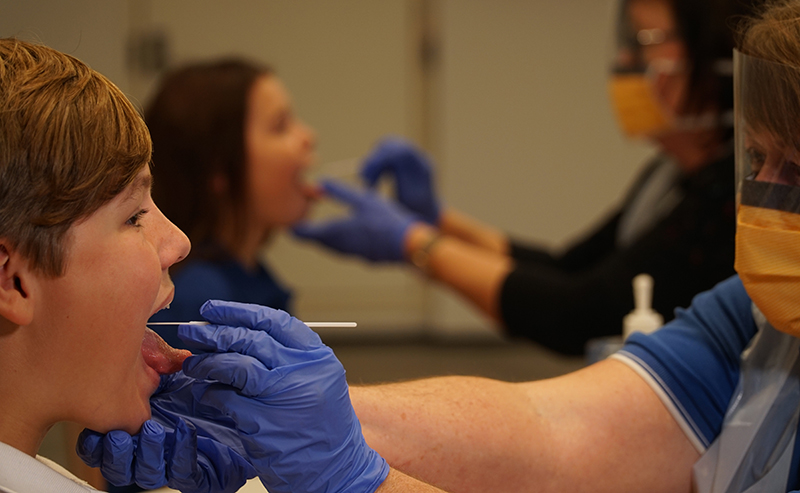
The DETECT Schools program is underway, with swabs taken at 13 of the participating schools across Western Australia. No asymptomatic COVID-19 has been detected to date.

The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers have collaborated with global experts to launch an online tool designed to assess the risk of contracting COVID-19 and provide advice to reduce transmission.

With COVID-19 restrictions starting to lift and families resuming some level of ‘normal life’, it is natural to have mixed feeling during this time, says The Kids mental health researcher.
